Pads¶
A pcb-pad statement represents a single electrical lead
interface in a pcb-landpattern.
Signature¶
pcb-pad pad-name (arg1:<Type1>, ...) :
name = <String>
description = <String>
type = <PadType>
shape = <Shape>
edge = <True|False>
layer(<LayerSpecifier>) = <Shape>
The expression name pad-name uniquely identifies this pad definition
in the current context.
The argument list (arg1:Type1, ...) is optional and provides a means of
constructing parameterized pad definitions.
- Required parameters
type- Pad type; eitherSMDorTHshape- Pad shape; aShapeexpression specifying the shape of the copper on all copper layers.- Optional parameters
name- Will be used in place of "pad-name" in the UI if available.description-Stringproviding metadata for thepaddefinition.edge- Sets if the pad is an edge connectorlayer- A layer statement defining the pad's geometry on a non-copper layer of the circuit board.
Usage¶
Here is a simple example of a parameterized pcb-pad:
a generator for BGA pads of specified diameter:
public pcb-pad bga-pad (diameter:Double) :
name = "SMD Pad"
type = SMD
val radius = diameter / 2.0
val pad-shape = Circle(radius)
; Pad is circular
shape = pad-shape
; Paste layer: Radius 5% smaller
layer(Paste(Top)) = expand(pad-shape, -(0.05 * radius))
; Check current design rules to get soldermask clearance
val soldermask-amount = clearance(current-rules(), SolderMaskRegistration)
; Soldermask layer is larger than pad
layer(SolderMask(Top)) = expand(pad-shape, soldermask-amount)
Our bga-pad definition constructs circular SMD pads by
computing the pad shape, then adding a slightly larger
circular soldermask layer.
We can use this to build a BGA landpattern.
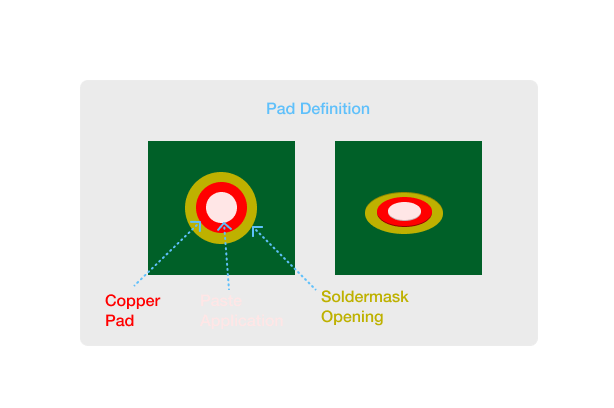
The image below shows the structure of our pad definition:
We use the expand function to construct soldermask outside
of the copper pad, and we reuse it with a negative parameter
to construct a paste layer inside of the pad.
Here is another example, this time of a non-plated through-hole pad:
; Non-plated TH pad
public pcb-pad npth-pad (drill-radius:Double) :
name = "NPTH-Pad"
type = TH
; Pad is circular
val hole-shape = Circle(drill-radius)
shape = hole-shape
layer(Cutout()) = hole-shape
The type statement specifies that it is a through-hole pad.
The Cutout() layer is the same shape as the pad itself, which
implicitly removes the pad and its plating.
Since it's non-plated we do not need to worry about a paste layer.
We could add a soldermask layer if needed.